Grand Canyon Conservancy | Grand Canyon Conservancy: National Park…
Page Load Speed
1.9 sec in total
First Response
96 ms
Resources Loaded
1.5 sec
Page Rendered
247 ms
About Website
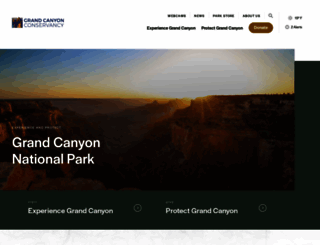
Visit grandcanyon.org now to see the best up-to-date Grand Canyon content for United States and also check out these interesting facts you probably never knew about grandcanyon.org
Interested in learning about how to experience and protect the Grand Canyon? If so, click to discover the work GCC does and how you can get involved.
Visit grandcanyon.orgKey Findings
We analyzed Grandcanyon.org page load time and found that the first response time was 96 ms and then it took 1.8 sec to load all DOM resources and completely render a web page. This is quite a good result, as only 35% of websites can load faster.